Skin concerns like hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone are common, especially among the Indian audience. If you’ve tried various home remedies without success, you might wonder when to consider skin whitening treatments. This comprehensive guide provides expert advice to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Skin Whitening
Skin whitening aims to reduce melanin production in the skin. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color, and its overproduction can lead to issues like dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
How Does Skin Whitening Work?

- Melanin Reduction: Treatments focus on decreasing melanin levels to lighten the skin tone.
- Tyrosinase Inhibition: Inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase reduces melanin synthesis.
- Exfoliation: Removing dead skin cells promotes new skin growth, leading to a brighter complexion.
- Collagen Production Stimulation: Some treatments boost collagen, improving skin texture and firmness.
Common Skin Concerns Addressed by Skin Whitening
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of the skin due to excess melanin. It can result from sun exposure, hormonal changes, or inflammation.
Dark Spots
Dark spots are small patches of skin that become darker than the surrounding area. They often result from acne scars or sun damage.
Uneven Skin Tone
An uneven skin tone means some areas of your skin are darker than others. This can be due to sun exposure or genetic factors.
Melasma
Melasma causes brown to gray-brown patches on the face. It’s often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy or sun exposure.
Sun Damage
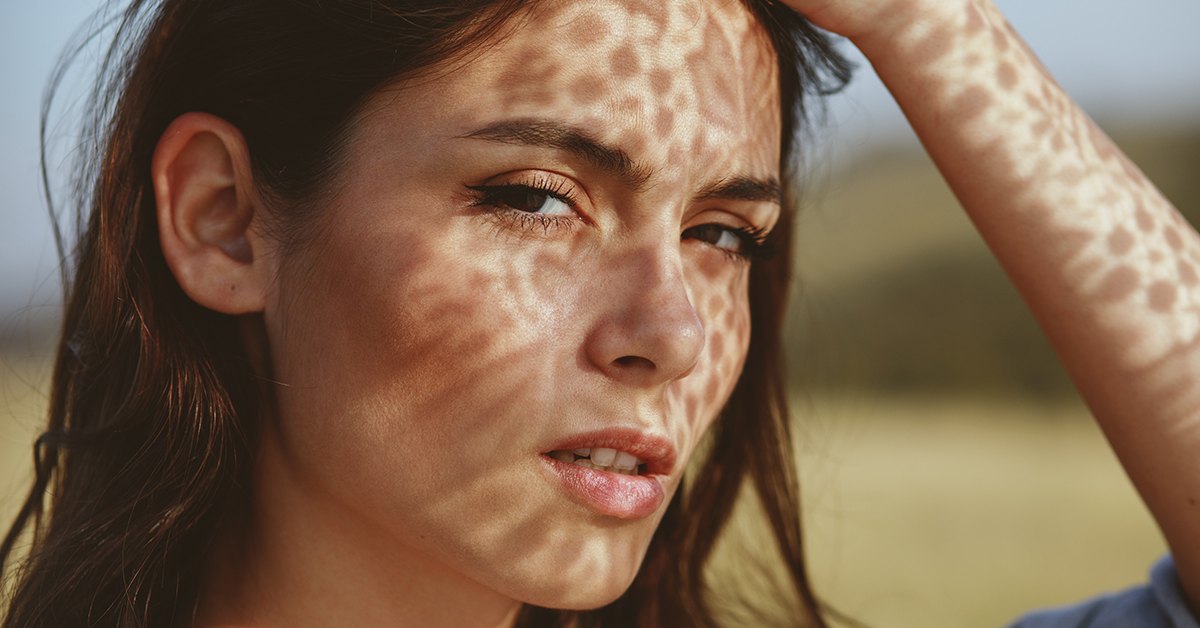

Prolonged sun exposure can lead to sun damage, causing dark spots and accelerating skin aging.
Age Spots
Also known as liver spots, age spots are flat, dark areas on the skin that appear in sun-exposed areas.
Acne Scars
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne can leave dark marks on the skin.
Professional Skin Whitening Treatments
Before opting for any treatment, a consultation with a dermatologist is crucial. They can assess your skin type and recommend the most effective and safe options.
Chemical Peels
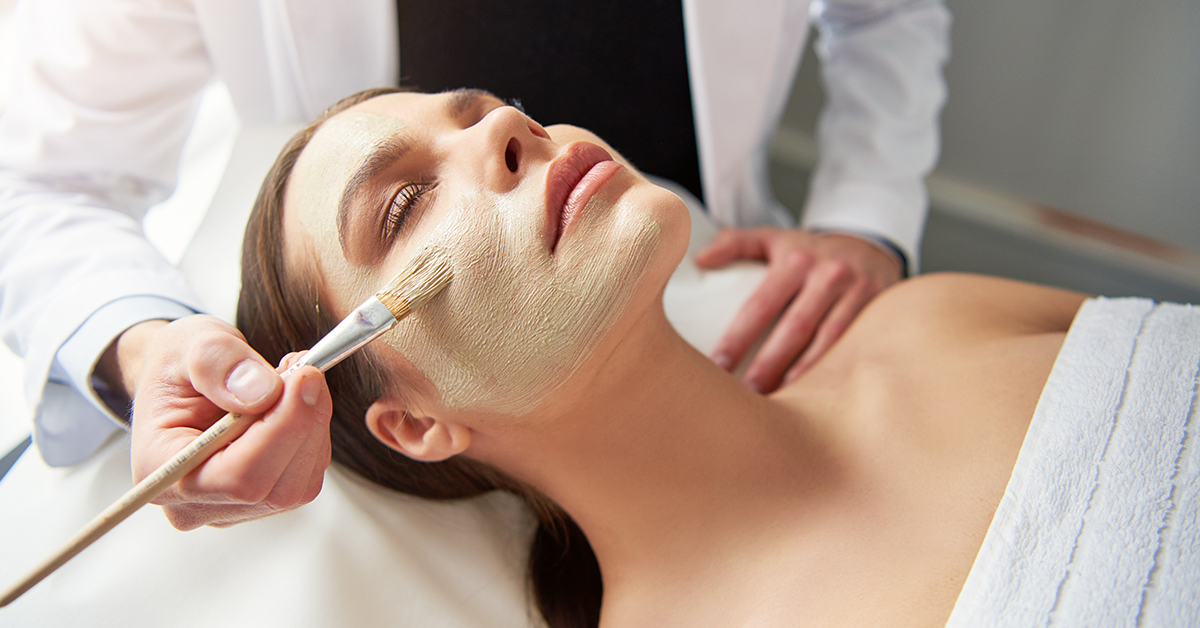

Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin. They help in melanin reduction by removing the outer layers of skin.
- Kojic Acid Peels: Derived from mushrooms, kojic acid inhibits tyrosinase, reducing melanin production.
- Glycolic Acid Peels: Glycolic acid exfoliates the skin, promoting an even skin tone.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy targets melanin deposits with concentrated light beams. It’s effective for hyperpigmentation and stimulating collagen production.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion uses a special device to gently exfoliate the skin, removing dead cells. It’s beneficial for uneven skin tone and dark spots.
Glutathione Injections
Glutathione injections are antioxidants that can reduce melanin production. They should be administered under professional supervision due to potential side effects.
Medi-facials
Medi-facials combine traditional facial techniques with medical-grade products. They can address specific concerns like hyperpigmentation.
Injectables
Injectables like skin boosters can hydrate the skin and improve its appearance.
Oral Agents
Certain oral agents, such as vitamin C supplements, can support skin whitening efforts by providing antioxidant properties.
Topical Treatments for Skin Whitening
Topical creams and serums are non-invasive options that can lighten the skin over time. They often contain active ingredients targeting melanin production.
Kojic Acid

Kojic Acid is effective in inhibiting tyrosinase, reducing melanin synthesis. It’s commonly found in skin lightening creams.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C offers antioxidant properties and can brighten the skin by reducing melanin formation.
Arbutin
Arbutin is a natural compound that inhibits melanin production. It’s gentler than hydroquinone and suitable for sensitive skin.
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a potent skin lightener that decreases melanin production. It’s effective but should be used under medical supervision.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic Acid helps treat hyperpigmentation and acne by reducing melanin production and exfoliating the skin.
Retinoids
Retinoids promote skin cell turnover and collagen production, improving skin texture and tone.
Licorice Extract
Licorice extract contains glabridin, which inhibits tyrosinase and reduces pigmentation.
Importance of Consulting a Dermatologist
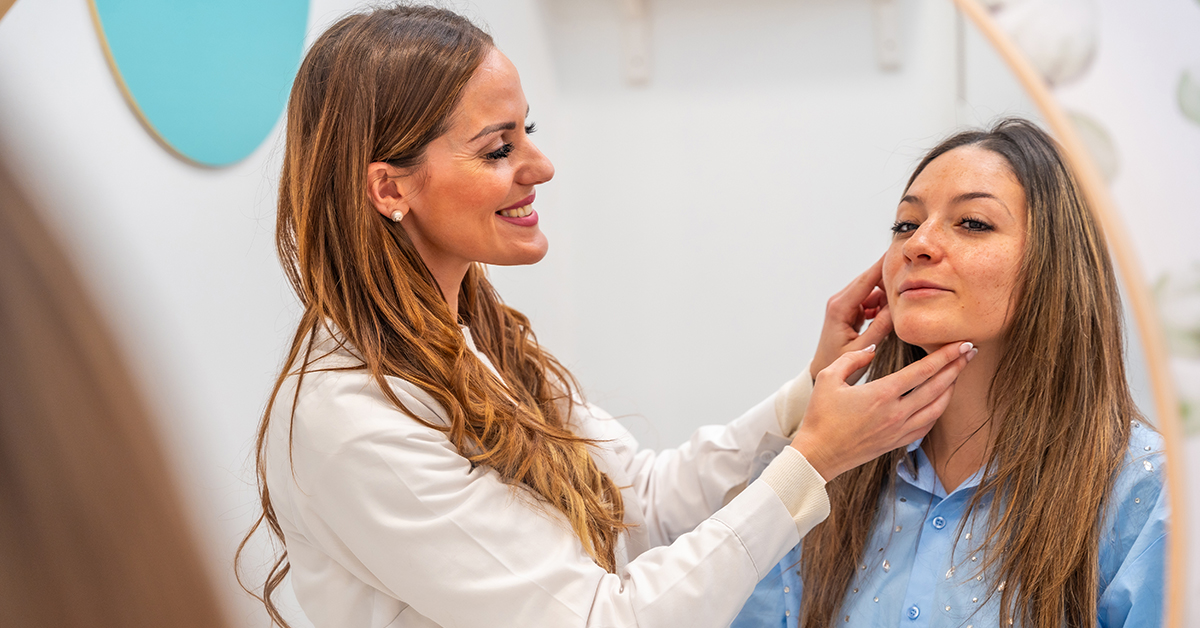

A consultation with a dermatologist ensures that you choose the right treatment for your skin type and condition. They can help minimize potential side effects.
Assessing Potential Side Effects
Every treatment has potential side effects, such as redness, irritation, or increased sensitivity. Understanding these risks is essential.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Dermatologists provide personalized plans that consider your medical history, skin type, and specific concerns.
Monitoring Progress
Regular check-ins allow for adjustments to your treatment, ensuring optimal results and managing any adverse reactions.
Post-Treatment Care
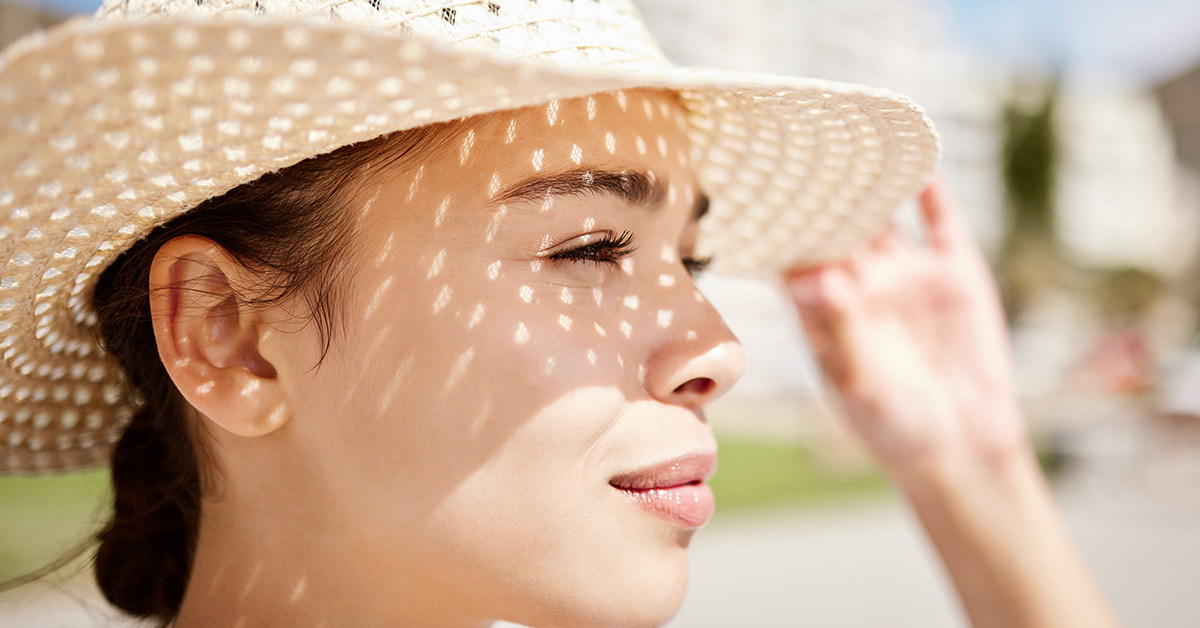

Proper aftercare maximizes the benefits of skin whitening treatments and maintains skin health.
Sun Protection
Sun protection is vital after treatments. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen to prevent sun damage and hyperpigmentation from returning.
Post-Treatment Guidelines
Follow your dermatologist’s instructions, which may include using gentle cleansers and avoiding harsh products.
When Should You Consider Skin Whitening Treatments?
Consider skin whitening treatments if:
- Over-the-counter products haven’t improved your skin concerns.
- Hyperpigmentation, dark spots, or uneven skin tone affect your confidence.
- You desire a more even complexion and have realistic expectations.
Remember, a consultation with a dermatologist is the first step.

Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Be aware of potential side effects like skin irritation, redness, or allergic reactions. Always inform your dermatologist about any allergies or skin sensitivities.

Conclusion
Skin whitening treatments offer solutions for various skin concerns, from hyperpigmentation to uneven skin tone. Professional treatments like chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can provide significant results. Topical options with ingredients like kojic acid and vitamin C are also effective. Always prioritize a consultation with a dermatologist to choose the best and safest treatment plan.
Citations
- Indian Journal of Dermatology: “Management of Hyperpigmentation” – Discusses treatments for hyperpigmentation in Indian skin types.
- Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology: “Topical Skin-Lightening Agents for Pigmentation Disorders” – Reviews efficacy of ingredients like kojic acid and arbutin.
- Dermatologic Surgery: “The Role of Laser Therapy in Treating Hyperpigmentation” – Explores laser treatments for skin lightening.
- Clinical Interventions in Aging: “Safety and Efficacy of Glutathione for Skin Whitening” – Evaluates the use of glutathione injections.
- British Journal of Dermatology: “Guidelines for the Safe Use of Hydroquinone” – Provides safety information on hydroquinone usage.
- American Academy of Dermatology: “Post-Procedure Skin Care” – Offers guidelines on caring for skin after treatments.





